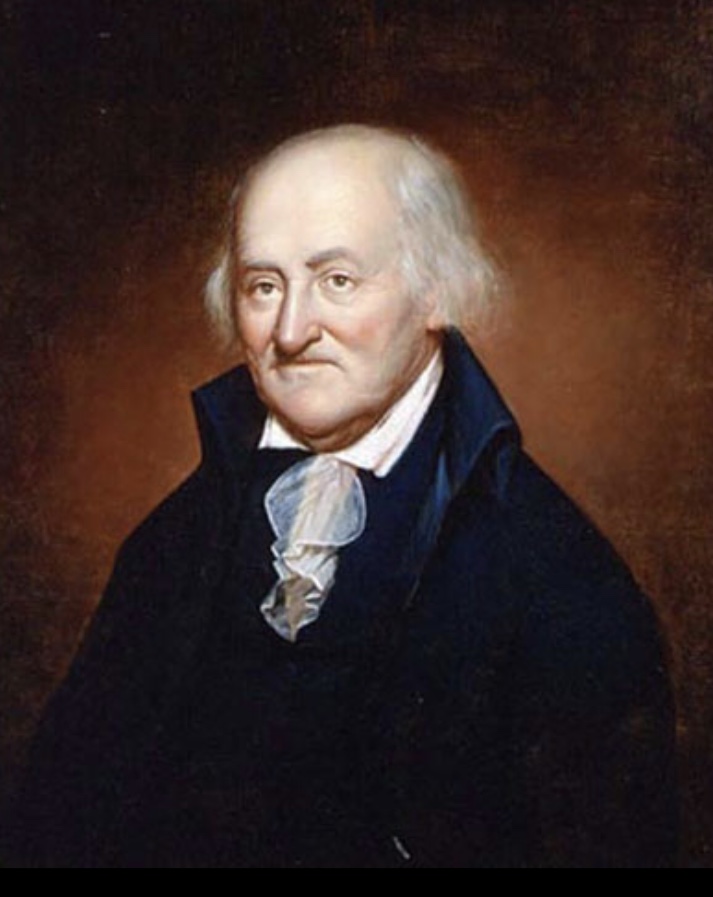Dear Reader,
Some chart news. Operation Cameo, book six in my Eve’s War Heroines of SOE series, is a top twenty hot new release in Britain. We will publish the book in February 2022. Many thanks to all my readers for their support.

This week I parcelled 84 books to send to the Bodleian Library, Oxford; Cambridge University Library; National Library of Scotland; Trinity College Dublin; The British Library and the National Library of Wales. Publishers have been fulfilling this requirement since 1662. A great tradition 🙂

Researching the Gadsden branch of my family I discovered grocers in London and Newport Pagnell. Further research revealed that earlier they had been traders in Liberia, Nevis and South Carolina.
Here’s Christopher Gadsden (16 February 1724 – 28 August 1805) an American politician who was the principal leader of the South Carolina Patriot movement during the American Revolution. He was a delegate to the Continental Congress, a brigadier general, Governor of South Carolina, a merchant and the designer of the Gadsden flag. He was also a signatory to the Continental Association and a Founding Father of the United States.
More about the Gadsdens in future posts.
I reckon I should award the prize for my most exotically named ancestors to Zephaniah Thorpe and his wife Mary Discipline.
The son of Ralph Thorpe and Mary Wakefield, Zephaniah was baptised on 25 April 1790 in Lakenham, Norfolk. He was named after his grandfather, Zephaniah.
Mary Discipline was born on 25 January 1789 and baptised on 1 February 1789 in Heacham, Norfolk. Her parents were Thomas Discipline and Mary Smith.
Zephaniah Thorpe and Mary Discipline married on 22 August 1813 in St Dunstan, Stepney, which indicates that they had moved from Norfolk to London. However, this was a small step before they embarked on an even greater adventure. Before detailing that adventure it is worth noting that Zephaniah and Mary signed their names on their marriage certificate. For a well-to-do man this was common, but for a woman, even one from the middle classes, it was a rarity. Often, women of the age were not taught how to read or write for fear that it would ‘corrupt’ their minds.
In 1829, Zephaniah and Mary found themselves in New York. You would think that emigration was a ‘young man’s game’, but Zephaniah was 39 and Mary 40 when they embarked on their journey. What compelled them to leave? For settlers in earlier centuries religious persecution offered the main motivation, but in Zephaniah and Mary’s case it would seem that a better quality of life was the main factor.
Zephaniah had a skill – he was a sculptor specialising in marble. In the 1830s New York was a developing city with a need for artisans. Zephaniah and New York were made for each other, so he took the gamble and transferred his family across the Atlantic Ocean.
Using a chisel, sculptors would remove large portions of unwanted stone. During this roughing out phase they would work rhythmically ensuring that the stone was removed quickly and evenly. Some artists would carve directly on to the stone while others used a model formed from wax or clay.
An example of a sculpture created during Zephaniah’s era can be found in Green-Wood Cemetery. There is no evidence that Zephaniah worked on this sculpture, but he definitely saw it and maybe it offered him some inspiration.
The sculpture is called Charlotte Canda (3 February 1828 – 3 February 1845). It’s a memorial to a young debutant, Charlotte, who died in a horse carriage accident on her way home from her seventeenth birthday party.
On 11 April 1838 at the Common Pleas Court in New York, Zephaniah and Mary applied for naturalisation. The application, sponsored by James Bryson, was granted and Zephaniah settled his family in Brooklyn.
In 1855 Zephaniah was living at Number 59 Ward 7, New York with his wife, Mary, their son, Thomas aged 39, a lodger Bartu Durando a jeweller from New Jersey also aged 39, and granddaughter Josephine A Thorp aged 10.
The street contained families from Canada, Germany, Ireland and Prussia plying their trades as bookkeepers, carpenters, clerks and grocers. A cosmopolitan area. Zephaniah’s son Thomas was also a sculptor. What did father and son sculpt? Probably the great marble columns and artefacts in New York’s burgeoning churches and civic buildings. Certainly, there was plenty of work available because by this time they had been plying their trade for 26 years.
Ten years later, Zephaniah, Mary, Thomas and Josephine were living in Brooklyn, in a house valued at $800. In this census Josephine was described as a niece from Alabama. Ten years earlier the census had described her as a grandchild. Official records are not always accurate, sometimes through accident, other times through design – particularly when people wish to hide something. Often, you need to read between the lines. There is no record of Thomas’ wife, so I’m inclined to believe that she died young and that Josephine was Thomas’ daughter. Certainly, she lived with him throughout her childhood.
Zephaniah died in Kings, New York on 9 September 1868 aged 80. He was buried in Green-Wood Cemetery, Brooklyn, Kings County, New York.
A Brooklyn directory of 1877 listed Mary as the widow of Zephaniah. It also listed Thomas as a sculptor, living at the same address. Josephine was not listed so it’s fair to assume that she had married and started her own family.
Mary died on 3 September 1876 of pneumonia at 287 Jay Street, Kings, New York. She was buried with Zephaniah in Green-Wood. By this time she had lived amongst the tall buildings of New York for 47 years, a far cry from her birthplace in the flat Norfolk Broads.
As ever, thank you for your interest and support.
Hannah xxx
For Authors
#1 for value with 565,000 readers, The Fussy Librarian has helped my books to reach #1 on 32 occasions.
A special offer from my publisher and the Fussy Librarian. https://authors.thefussylibrarian.com/?ref=goylake
Don’t forget to use the code goylake20 to claim your discount 🙂